Hyperconvergence vs. Converged Infrastructure
What's the Difference and Which One Is Right for You?
When
it comes to data center infrastructure, there are two main approaches:
converged infrastructure and hyper-converged infrastructure. While these terms
may sound similar, they actually represent two different ways of building and
managing data center resources. In this blog, we'll take a closer look at the
differences between converged infrastructure and hyperconverged infrastructure
and help you decide which one is right for your organization.
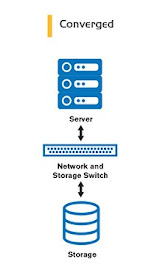
What is Converged Infrastructure?
Converged infrastructure is designed to simplify data center operations by reducing the number of vendors and components that must be managed. This can result in lower costs, easier management, and faster deployment times. However, converged infrastructure can also be more rigid than other solutions, as it may not be able to adapt to changing requirements as easily as other solutions.
What is
Hyperconverged Infrastructure?
HCI
is designed to provide a more flexible and scalable solution than converged
infrastructure. Because the storage and computing resources are integrated into a
single appliance, it is easier to scale up or down as needed. Additionally,
because the storage is software-defined, it is easier to manage and can be
configured to provide more advanced features such as data deduplication,
compression, and replication.
Hyperconvergence
vs. Converged Infrastructure: Key Differences
While
converged infrastructure and hyperconverged infrastructure share many
similarities, there are some key differences to consider:
- Integration: Converged
infrastructure typically consists of pre-integrated hardware components
from multiple vendors, whereas hyperconverged infrastructure integrates
storage, computing, and networking resources into a single appliance.
- Scalability: Hyperconverged
infrastructure is typically more scalable than converged infrastructure,
as it is easier to add or remove resources as needed.
- Flexibility: Hyperconverged
infrastructure is generally more flexible than converged infrastructure,
as it can adapt to changing requirements more easily.
- Complexity: While both converged infrastructure and hyperconverged infrastructure aim to simplify data center operations, hyperconverged infrastructure can be more complex to implement and manage due to the software-defined storage layer.
Which One is Right for You?
Deciding between converged infrastructure and hyperconverged infrastructure depends on a number of factors, including your organization's size, budget, and specific needs. Here are some factors to consider:
- Size: If you have a
smaller data center with fewer resources, converged infrastructure may be
a good option as it can provide a simpler, more cost-effective solution.
However, if you have a larger data center or need to scale quickly,
hyperconverged infrastructure may be a better choice.
- Budget: Converged infrastructure
can be a more cost-effective solution, as it allows you to take advantage
of existing hardware investments. However, hyperconverged infrastructure
may provide a better return on investment over time due to its scalability
and flexibility.
- Specific Needs: Consider the
specific needs of your organization when deciding between converged and
hyperconverged infrastructure. If you need more advanced storage features
or want a more flexible solution, hyperconverged infrastructure may be the
better choice. However, if you have a specific hardware or vendor
preference, converged infrastructure may be the way to go.
The Role of
Hyperconvergence in Supporting AI and Machine Learning Workloads
Artificial
Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) workloads are becoming increasingly
popular in modern business environments. These workloads require significant
computing power and storage capabilities to process large amounts of data and
deliver results in real time. Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) is emerging as
a powerful solution to support these workloads, providing the necessary
resources and flexibility to handle the demands of AI and ML.
Why
Hyperconvergence is Ideal for AI and ML Workloads
AI
and ML workloads require high-performance computing and storage resources.
Hyperconverged infrastructure provides a scalable and flexible platform that
can easily be tailored to meet the specific needs of these workloads. Unlike
traditional IT infrastructures, HCI allows organizations to quickly and easily
scale resources up or down as needed. This makes it an ideal platform for
businesses that are looking to deploy AI and ML applications, which often
require high levels of computational power, memory, and storage.
HCI
also supports the use of virtualization technology, which is a key component of
AI and ML workloads. By running these workloads in virtual environments,
businesses can take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of HCI while
still maintaining the necessary levels of performance and reliability.
Another
benefit of HCI for AI and ML workloads is the ability to use software-defined
storage solutions. These solutions allow businesses to easily manage and store
large amounts of data, which is critical for AI and ML workloads that rely on
data analysis and processing. With software-defined storage, businesses can
store data in a more efficient and cost-effective manner, while still
maintaining the necessary levels of performance and reliability.
Hyperconverged
infrastructure also provides businesses with the ability to rapidly deploy new
applications and services, including AI and ML applications. By using HCI,
businesses can reduce the time and effort required to deploy new applications,
allowing them to take advantage of emerging technologies and gain a competitive
edge in their markets.
Key
Considerations for Implementing HCI for AI and ML Workloads
Implementing
HCI for AI and ML workloads requires careful planning and consideration. Some
key considerations include:
- Hardware
requirements: When deploying HCI for AI and ML workloads, it is important
to carefully consider the hardware requirements needed to support these
workloads. This may include high-performance CPUs, large amounts of
memory, and high-capacity storage solutions.
- Software-defined
storage: To effectively support AI and ML workloads, businesses may need
to consider using software-defined storage solutions. This can help to
optimize storage performance and provide the necessary levels of
scalability and flexibility.
- Networking requirements:
AI and ML workloads often require high-bandwidth networking to support
data transfer and analysis. Businesses may need to consider upgrading
their networking infrastructure to support these workloads.
- Virtualization
technology: HCI platforms rely heavily on virtualization technology. It is
important to carefully consider the virtualization technology needed to
support AI and ML workloads, including hardware-assisted virtualization
and nested virtualization.






Comments
Post a Comment